As cities continue to grow and new developments rise, ensuring fire safety compliance becomes both more challenging and more essential. Modern building owners and managers must not only keep up with updated fire codes but also harness advanced technologies to maximize occupant safety. Partnering with industry leaders like Brycer can streamline compliance workflows, helping property professionals stay ahead of the curve in safeguarding lives and assets.
The dynamic nature of fire safety requirements means that adaptation is key. New materials, data-driven alarm systems, and enhanced regulatory oversight all play crucial roles in this evolving landscape. With so much at stake, it is vital to understand how regulatory changes, smarter technologies, and lessons from recent fires are shaping the future of fire protection. This article examines key areas of change and explores what stakeholders need to know to maintain robust fire safety standards.
Modern Multifamily Buildings: A Safer Choice
Over the past decade, data have clearly shown that modern multifamily buildings provide better fire safety results compared to single-family homes and older apartments. Fatalities from fires in new multifamily structures are six times less common than in single-family houses or older units. This improvement comes from better fire-resistant construction, integrated sprinkler systems, improved means of escape, and consistent adherence to strict modern codes.
Developers have responded to stricter code enforcement and the demand for safer living spaces by incorporating a range of safety measures throughout the design and construction process. These improvements help isolate incidents, giving first responders and residents more time to act, and have been crucial to the decline in fire-related injuries and deaths in recent years.
Importantly, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are as vital as the initial installation. Frequent inspections and mandatory fire drills further reduce the risk of fatal incidents, reinforcing the value of proactive management in these safer living environments.
An added benefit of these codes and methods is the scalability for dense urban areas, where multifamily units comprise the majority of new residential construction. With this trend, the lessons learned from safer buildings can be applied on a large scale, saving more lives as urbanization intensifies.
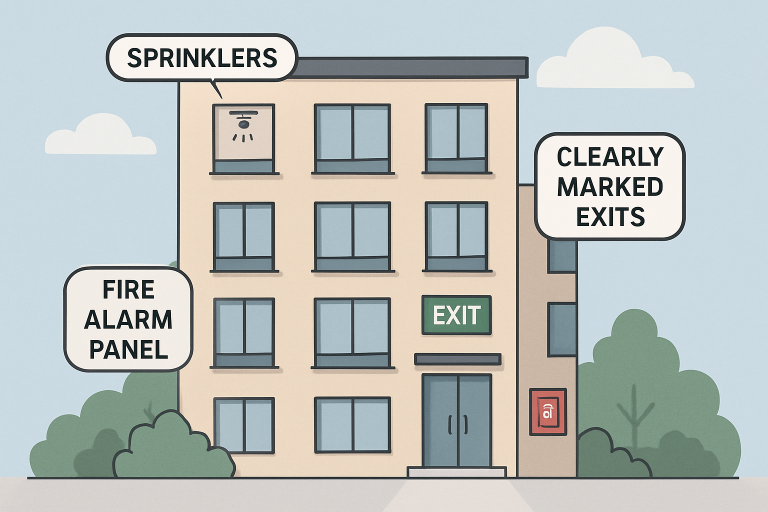 Regulatory Updates: Staying Ahead of Compliance
Regulatory Updates: Staying Ahead of Compliance
The regulatory environment for fire safety continues to tighten as new risks and failures come to light. The 2026 fire code update will require smart fire alarm systems capable of real-time monitoring, automated fault reporting, and improved incident detection. These changes aim to address common pain points, such as delayed emergency responses and high false alarm rates, by enabling property managers and first responders to receive precise, up-to-the-minute information when a fire occurs.
Additionally, inspections are becoming more frequent and comprehensive. Fire protection systems, previously inspected annually or biannually, are now subject to quarterly or monthly reviews depending on their complexity and the building’s occupancy profile. These rigorous schedules help ensure alarms, sprinklers, and emergency exits are always operational and highlight the necessity for digital recordkeeping and automated compliance tracking.
This surge in requirements can be daunting for property owners, but technology partners and compliance management solutions simplify the task, reducing the risk of costly violations and increasing life safety.
Advancements in Passive Fire Protection Technologies
Passive fire protection forms the bedrock of building safety by preventing the rapid spread of fire and smoke through a structure. Recent advances include fire doors with more robust core materials, automated sealing thresholds, and improved compartmentation designs that contain blazes within single units or floors. These innovations are essential because inadequate fire door integrity and improper installation are the two leading causes of passive protection failure, with over 40 percent of fire doors failing recent integrity tests.
New standards now require certified installation and routine door checks, addressing historic gaps and promoting greater reliability. Additionally, non-combustible insulation, intumescent coatings, and advanced cable management systems are helping to further limit the propagation of heat and smoke, not just fire itself, between building zones. The attention given to these passive methods represents a significant step forward in construction and maintenance, reducing evacuation time and protecting critical escape routes.
Case Studies: Lessons from Recent Incidents
2023 Dubai Apartment Fire
In April 2023, a residential fire ripped through a Dubai apartment complex, resulting in 16 fatalities. Investigations found that the root causes were non-compliance with fire safety regulations, inadequate routine checks, and a lack of functioning alarms in shared spaces. This tragedy highlights the risks of falling behind on inspections and failing to modernize life-safety systems. Timely adoption of updated fire codes and maintenance protocols could have drastically reduced the loss of life.
2022 Bronx Apartment Fire
The Bronx fire in January 2022 was caused by a malfunctioning electrical space heater in a high-rise apartment. Seventeen residents lost their lives due to a combination of faulty fire doors and an inadequate heating system that led to widespread use of space heaters. The event drew global attention to the need for robust passive fire protection and for keeping fire-rated doors closed and operational at all times. The lessons learned underscore the importance of integrating technology, updating older systems, and enforcing ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
The evolving landscape of fire safety compliance demands a proactive, dynamic approach from everyone involved in modern building management. By keeping pace with regulatory updates, implementing the latest active and passive fire protection technologies, and learning from past failures, stakeholders can create safer, more resilient environments. Investing in compliance is not just about meeting requirements; it is a fundamental commitment to protecting the lives of building occupants now and in the future.