Understanding High-Altitude Airspace
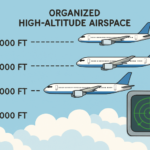
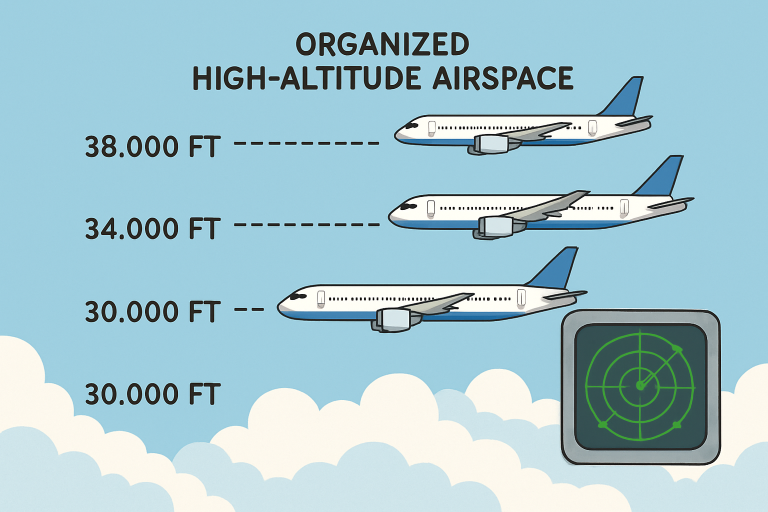
As the aviation industry continues to expand, efficient use of high-altitude airspace becomes increasingly critical. This region, generally defined as airspace above 29,000 feet (Flight Level 290 and above), is primarily utilized by commercial airlines and long-distance flights seeking optimal operational efficiency. The thin air at these altitudes helps reduce drag, which in turn improves fuel economy and enables aircraft to travel longer distances with fewer stops.
Today, high-altitude corridors are busier than ever, accommodating not only legacy airlines but also a growing number of new commercial operators and military flights. The increased density means that modern aviation demands sophisticated traffic management and international collaboration. For operators seeking compliance and safety in these tight environments, RVSM certification is a crucial step in preparing both aircraft and crew for the strict requirements of high-altitude flight.
With the continued expansion of the aviation sector, the need for more strategic allocation of altitudes and precise aircraft separation has never been more urgent. The safe, efficient, and sustainable operation in this portion of the sky relies significantly on advanced systems and international standards for separation, surveillance, and communication.
Moreover, shifting passenger demand patterns, cargo logistics, and the advent of longer-range commercial jets are further intensifying traffic at these flight levels. These factors place added pressure on airspace managers worldwide and necessitate new operational concepts and regulatory updates to keep pace with growth.
The Role of Reduced Vertical Separation Minima (RVSM)
One of the most transformative updates in high-altitude airspace management is the adoption of Reduced Vertical Separation Minima (RVSM). Previously, aircraft operating above 29,000 feet were separated vertically by 2,000 feet to allow for navigational inaccuracies and improve safety margins. With modern avionics improvements and stricter certification standards, RVSM has reduced this vertical separation to 1,000 feet, effectively doubling the number of usable flight levels within congested segments.
RVSM allows air traffic controllers to accommodate more aircraft in the same volume of airspace without compromising safety. This operational gain enables airlines to select more optimal altitudes for fuel savings and operational needs, which has major impacts on financial and environmental costs. As air traffic continues to intensify, such technological and procedural enhancements are indispensable.
 NextGen: Modernizing Air Traffic Management
NextGen: Modernizing Air Traffic Management
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has launched a sweeping initiative known as the Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen). NextGen replaces decades-old radar surveillance and analog voice communications with state-of-the-art digital navigation and communication systems. Satellite-based technology now delivers real-time, precise aircraft tracking, allowing controllers and flight crews to identify optimal routing and altitude paths while minimizing delays.
One of NextGen’s core benefits is the ability to plot more direct and flexible flight plans, reducing unnecessary fuel burn and cutting in-flight time. The digital infrastructure also enhances communication between pilots and ground controllers, enabling more agile decision-making in changing weather or traffic conditions.
Integrating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
The rapid emergence of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), often called drones, is presenting new opportunities and challenges for managing high-altitude airspace. From defense applications to commercial logistics, UAVs increasingly operate in areas that overlap with traditional commercial flight paths. Integrating these vehicles safely is forcing regulatory bodies to rethink rules for traffic separation, collision avoidance, and communication protocols.
Developing robust protocols for UAV operations at high altitudes is necessary to avoid any conflict between manned and unmanned aircraft. This includes establishing dedicated corridors, employing advanced sense-and-avoid technology, and harmonizing regulations among international authorities, which is an evolving area of global aviation policy.
Environmental Considerations
Optimizing high-altitude airspace offers substantial environmental benefits, especially amid growing pressure to reduce aviation greenhouse gas emissions. Efficient management leads to more direct flight paths, reduced holding and stacking patterns, and less congested skies, resulting in tangible reductions in fuel burn and carbon emissions. According to the Airspace Change Organisation Group, Europe’s recent airspace modernization efforts are projected to save up to 18 million tonnes of CO2 annually.
These improvements serve not only airlines and passengers but also answer the increasing demand from governments and the public for more responsible air transport solutions. Environmental stewardship is quickly becoming a central component in airspace design and modernization initiatives around the globe.
Challenges in Airspace Modernization
Even with clear benefits, the path toward modernized high-altitude airspace presents significant challenges. Large-scale updates to communication and surveillance systems require extensive investment, while rapid technological changes demand continuous training and adaptation among all stakeholders. Ensuring the interoperability of new systems across airlines, nations, and regulatory boundaries is a complex, ongoing task.
Additionally, increased reliance on digital technologies introduces new security risks. Securing air traffic management networks from cyber threats is now a mission-critical priority for all airlines and aviation authorities, requiring robust protocols, encryption, and coordinated incident response planning.
The Future of High-Altitude Airspace Management
The future of efficient airspace management lies in leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning. These tools can forecast traffic trends, anticipate potential conflicts, and automatically propose reroutes long before controllers or pilots are even aware of an issue. International collaboration will be necessary to establish comprehensive regulations and data-sharing standards across all borders, ensuring the skies remain safe and efficient as aviation evolves further.
Conclusion
Efficient high-altitude airspace management is at the core of modern aviation’s promise for safety, sustainability, and progress. Through advancements like RVSM and NextGen, the careful integration of UAVs, and a renewed focus on environmental stewardship, the industry is preparing to meet tomorrow’s challenges head-on. Continued innovation, collaboration, and vigilance will be key to ensuring that our increasingly crowded skies remain orderly and safe well into the future.