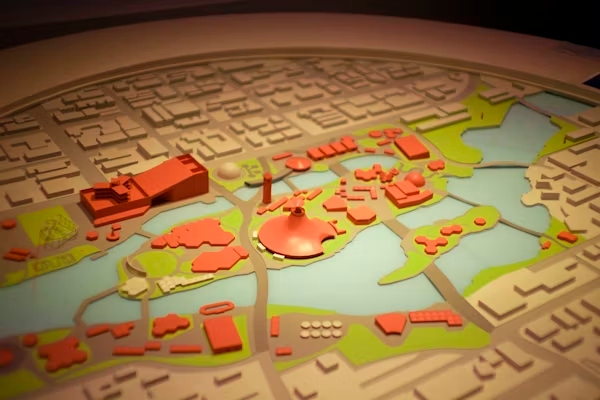
In an era defined by rapid urbanization and environmental uncertainty, Tarnplanen has emerged as a comprehensive framework that reshapes the way societies approach sustainable planning. The term Tarnplanen, derived from Scandinavian roots meaning “shield plan” or “protective strategy,” refers to an integrated system for balancing human development with ecological preservation. It encompasses methodologies for managing urban expansion, conserving natural resources, and mitigating the effects of climate change. Through innovation, data-driven insights, and community engagement, Tarnplanen is revolutionizing how governments, industries, and citizens collaborate toward a more resilient future.
The Concept of Tarnplanen
Tarnplanen is more than a policy model—it is a philosophy that emphasizes protection through preparation. It operates on the belief that sustainable progress must stem from foresight, precision, and adaptability. At its core, Tarnplanen aligns urban planning, environmental protection, and technological innovation under a unified vision. Instead of addressing issues reactively, it encourages stakeholders to anticipate environmental risks, predict urban challenges, and implement protective strategies long before problems escalate.
This proactive orientation distinguishes Tarnplanen from conventional approaches. It seeks to ensure that development projects—be they industrial, residential, or agricultural—proceed only after evaluating their long-term environmental consequences. By embedding predictive analytics and risk modeling, Tarnplanen allows planners to simulate potential outcomes and optimize land use without compromising ecological balance.
Origins and Evolution
The roots of Tarnplanen trace back to Northern Europe’s environmental reforms of the early 21st century. As climate awareness deepened across Scandinavia, policymakers began integrating ecosystem resilience into urban and regional planning. Tarnplanen emerged as a synthesis of these efforts—a tool designed to bridge the gap between environmental science and strategic governance.
Initially, the framework focused on flood defense systems, forest preservation, and sustainable architecture. However, as technological capabilities expanded, Tarnplanen evolved into a multidisciplinary strategy incorporating geospatial data, AI-driven modeling, and renewable energy integration. Today, it is used not only in environmental conservation but also in sectors such as transportation, waste management, and energy policy.
Core Principles of Tarnplanen
Several guiding principles define the Tarnplanen framework:
-
Preventive Action Over Remediation
Tarnplanen advocates for interventions before damage occurs. By assessing environmental vulnerabilities early, planners can prevent degradation instead of paying the high cost of recovery later. -
Holistic Integration
The framework integrates ecology, economy, and society, ensuring that each policy supports long-term sustainability. It rejects isolated planning models in favor of interconnected systems. -
Community and Stakeholder Engagement
Tarnplanen emphasizes the inclusion of local communities in the decision-making process. Citizen participation enhances accountability and ensures that projects reflect regional needs. -
Technological Intelligence
Data-driven tools—such as satellite monitoring, AI modeling, and digital twins—are essential for predictive analysis and scenario planning under Tarnplanen. -
Resilience and Adaptability
The approach values flexibility, allowing plans to evolve with new data, social trends, and environmental conditions.
Tarnplanen in Urban Contexts
Modern cities face increasing challenges: rising temperatures, reduced biodiversity, and unsustainable infrastructure expansion. Tarnplanen addresses these concerns through urban resilience strategies. For instance, it promotes the creation of green belts, eco-corridors, and water retention zones to counter urban heat and flooding.
Cities adopting Tarnplanen methodologies prioritize low-impact design—developments that use renewable materials, minimize carbon emissions, and maintain harmony with surrounding ecosystems. Urban planners employ the framework to redesign transportation systems, aiming for energy efficiency and reduced congestion through electric public transport and smart mobility networks.
Moreover, Tarnplanen integrates circular economy concepts into urban policy. Waste materials are reused, water is recycled, and buildings are designed for longevity. These elements collectively enhance sustainability while improving the quality of life for urban residents.
Environmental Protection and Resource Management
Beyond cities, Tarnplanen has profound implications for natural landscapes. It serves as a roadmap for ecosystem conservation, enabling authorities to designate protected zones based on environmental sensitivity and biodiversity data. Forest management under Tarnplanen ensures reforestation, sustainable logging, and the preservation of wildlife corridors.
In agricultural regions, the framework promotes precision farming, where resource use—especially water and fertilizers—is optimized to reduce waste and soil degradation. Renewable energy generation, particularly solar and wind, is planned in tandem with land conservation measures, preventing ecological disruption.
Importantly, Tarnplanen encourages interregional collaboration in managing shared ecosystems such as river basins, coastal areas, and mountain ranges. This cooperative dimension fosters ecological stability across borders and enhances climate resilience at a continental scale.
The Role of Technology in Tarnplanen
Technology functions as the nervous system of Tarnplanen. Through advanced geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing, planners can monitor deforestation, track pollution levels, and predict the impacts of extreme weather events. Artificial intelligence algorithms analyze these data sets, enabling policymakers to visualize future scenarios and make evidence-based decisions.
The rise of digital twin technology—virtual replicas of physical environments—has been particularly transformative. Urban regions can now simulate how proposed buildings, transport routes, or energy systems will affect air quality and biodiversity. This predictive modeling not only saves time and money but also minimizes environmental risks before construction begins.
Additionally, blockchain systems are being explored for environmental transparency under the Tarnplanen model. They provide traceable data on resource usage and carbon emissions, ensuring that sustainability claims are verifiable and accountable.
Economic and Social Dimensions
While Tarnplanen is environmentally focused, it also brings significant economic and social benefits. Green infrastructure projects create employment opportunities in renewable energy, sustainable construction, and environmental research. The framework supports eco-innovation, encouraging startups and industries to design products aligned with sustainability goals.
Socially, Tarnplanen nurtures community resilience. By engaging citizens in environmental stewardship, it fosters a sense of shared responsibility. Educational programs linked to Tarnplanen teach future generations the importance of coexistence with nature, ensuring continuity of its principles.
Furthermore, regions adopting Tarnplanen often experience improved public health due to cleaner air, reduced noise, and greater access to natural spaces. These indirect benefits contribute to the overall well-being of society, reinforcing the value of environmental planning.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its strengths, Tarnplanen faces obstacles. Implementation can be hindered by political inertia, funding limitations, and uneven technological access across regions. Developing countries may struggle to adopt such comprehensive systems due to infrastructural and institutional gaps.
However, international collaboration and digital innovation are bridging these divides. Global environmental organizations are working to adapt Tarnplanen principles to diverse socio-economic contexts. As data technologies become more affordable and accessible, even smaller municipalities can integrate predictive and adaptive planning tools.
Looking ahead, Tarnplanen is expected to become a universal planning standard. Its principles are being integrated into climate adaptation strategies, smart city initiatives, and global sustainability goals. With increasing environmental awareness, the framework’s relevance is likely to grow exponentially in the coming decades.
Conclusion
Tarnplanen stands as a beacon of modern environmental strategy—one that blends science, technology, and social responsibility. It illustrates that sustainable development is not merely an aspiration but a systematic process grounded in foresight and cooperation. By promoting resilience, inclusivity, and innovation, Tarnplanen transforms the traditional paradigms of planning into a forward-thinking, data-informed movement. Ultimately, its philosophy reminds us that the best way to safeguard the future is to plan for it today, with both nature and humanity in mind.