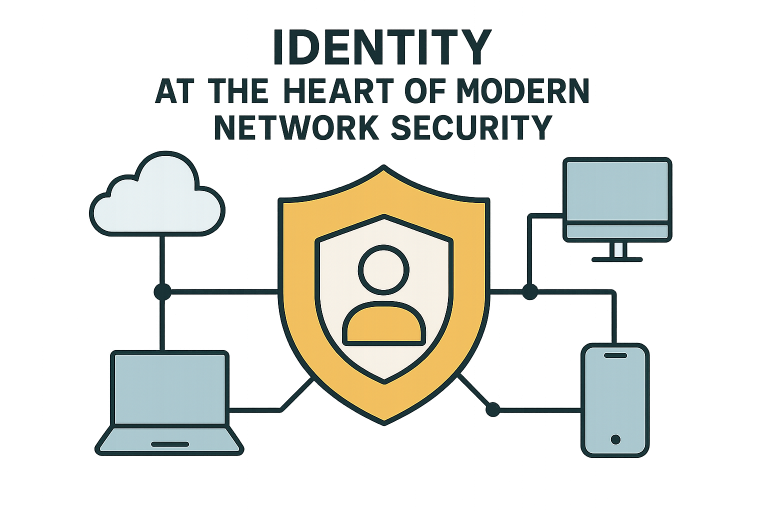
Understanding Identity-Driven Security
The rapid evolution of network architectures—driven by cloud migration, remote work, and mobile access—has diminished the security value of physical perimeters. In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding digital assets means focusing on who or what is accessing your network. Identity-driven security redefines access control by verifying and managing individual users and devices, ensuring security doesn’t rely on location or underlying infrastructure.
Solutions such as the Versa Networks SASE platform play a pivotal role by integrating identity-based access with advanced networking and threat protection. These platforms help organizations extend robust security to users wherever they are, unifying policy enforcement and identity verification for a seamless and consistent security posture.
Simply put, identity-driven security treats every access request as an independent trust decision. Whether a user connects from inside the office or halfway across the globe, the same rigorous evaluation applies—ensuring that only authorized users and trusted devices are allowed through.
Security teams are embracing this paradigm not just for enhanced protection, but also for the agility it provides. With identity at the core of access control, organizations can quickly adapt to changing personnel, devices, and cloud resources while retaining strict control over who is allowed into their most sensitive environments.
The Shift to Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has emerged as the gold standard for modern security frameworks. Instead of assuming any user or device is trustworthy by default, ZTA enforces a “never trust, always verify” approach. Each connection attempt is evaluated in real time, continuously checking for valid credentials, device health, and security posture.
This shift is not merely theoretical; research shows that adopting Zero Trust can significantly lower the risk of both insider and external threats. Organizations implementing Zero Trust report fewer successful data breaches and reduced lateral movement by attackers once inside the network.
 Addressing the Rise of Identity-Based Attacks
Addressing the Rise of Identity-Based Attacks
Cybercrime has shifted its tactics: instead of relying on malware, attackers now favor credential theft, phishing, and social engineering. According to security industry reports, 79% of attacks in 2024 were malware-free, with a focus on weak or stolen identities as the entry point. This change in threat dynamic means legacy perimeter defenses are inadequate—modern defenses must identify risky behavior, compromised credentials, and anomalous access patterns.
Organizations that fail to adapt can face devastating consequences. High-profile breaches in recent years, including supply chain attacks and massive credential leaks, have underscored the urgent need for robust identity controls, continuous authentication, and swift response capabilities.
Integrating AI in Identity Security
Artificial Intelligence is transforming how companies detect and prevent cyber threats. In an identity-driven approach, AI engines analyze vast streams of authentication and behavioral data, identifying signs of compromise or unusual activity in real-time. These systems can spot anomalies—such as a user logging in from two countries simultaneously or accessing sensitive files outside regular hours—before manual defenses would even notice.
Industry partnerships, such as those between leading identity and cybersecurity firms, are driving significant improvements in both the speed and accuracy of threat detection. For instance, alliances between cloud identity providers and advanced threat platforms enable a “defense in depth” model, leveraging AI to fight AI-driven attacks with greater efficacy and scale.
Implementing Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) is an emerging field that focuses on defending identity management systems against direct attacks. ITDR combines prevention, detection, and automated response—quickly spotting risks, resetting compromised credentials, and reviewing access logs to stop threats early. These solutions are especially important in hybrid and remote work environments, where identity often serves as the main, and sometimes only, line of defense.
Practical ITDR tools monitor both routine and advanced attacks, ranging from password spraying and credential stuffing to sophisticated lateral movement within identity directories. By automating responses and orchestrating recovery, organizations dramatically reduce the mean time to detect and remediate identity-based threats.
Challenges in Identity Management
Scaling identity management presents unique challenges, particularly in organizations that adopt multi-cloud or hybrid environments. Integrating diverse user directories, synchronizing policies, and preserving seamless user experiences require well-architected identity platforms and carefully crafted policies.
Privacy remains a crucial concern: organizations must rigorously define access levels and comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Balancing robust verification with user convenience and data minimization is essential. Additionally, ongoing employee training and awareness are fundamental to preventing social engineering and unintentional leaks.
Future Outlook
As organizations expand digital operations, the shift to identity-driven security will only intensify. The future will be shaped by deeper integration of AI-powered controls, widespread adoption of Zero Trust, and the evolution of identity fabrics that unify user, device, and workload identities across heterogeneous networks.
Cybersecurity leaders are prioritizing investments in identity management, automation, and advanced behavioral analytics. The ultimate goal is to create self-defending networks in which identity is not just a gatekeeper. Still, a strategic asset—proactively reducing risks, minimizing operational overhead, and enabling secure digital transformation.
Modernizing network security is no longer optional. Strong, identity-driven security strategies enable organizations to confront tomorrow’s sophisticated threats with resilience and confidence.
Conclusion
Identity-driven security has become the cornerstone of modern network defense, addressing the shortcomings of traditional perimeter-based approaches. By placing identity at the center, organizations can enforce Zero Trust principles, leverage AI for real-time threat detection, and implement ITDR to respond efficiently to identity-based attacks. Despite challenges in scaling and privacy, investing in robust identity management ensures adaptable, resilient, and secure digital environments. As networks continue to evolve, prioritizing identity as a strategic asset will be essential in safeguarding critical resources and supporting secure digital transformation.